"Make technology accessible, make the business flourish"- ClearCats ® redefines the future of eye care.
In the entrepreneurship sector, we have laid a solid foundation for the monetization of the project through systematic market analysis and accurate strategic planning. We used PESTEL analysis, Porter Five Force model, SWOT analysis, and other tools to comprehensively evaluate the market environment, competition landscape, and potential partners to ensure that the decision is scientific and forward-looking. In terms of financing, we have formulated a multi-stage investment strategy covering seed rounds to IPO, accurately matching the capital needs of different stages of development to ensure that the project has sufficient capital support from prototype development to global market expansion.
We focus on the two core groups of cataract patients and contact lens users, clarify value propositions, innovate promotion methods, and combine B2B and B2C channels, to expand product coverage. We enhance brand influence through authoritative endorsement, digital marketing, and public welfare linkage and create a reliable product image. We have planned a phased promotion path from pilot to globalization, built a partner ecosystem covering research and development, production, and public welfare, and improved the user support system to ensure continuous optimization and user satisfaction after launching the product.
In short, our work in the entrepreneurship section not only focuses on technological innovation, but also pays more attention to the dual realization of commercial feasibility and social value, striving to make every lens a step towards changing the world.
Market Analysis
PESTEL Analysis
Note: The following types of analysis are not from professional sources. When the actual project is implemented, it is necessary to seek help and support from the School of Economics. In the following attachment, I listed a series of experts, professors, and researchers that can be considered for advice, or if needed, we could seek analysis from graduate and doctoral students in the School of Economics. Multiple-party contact increases the possibility of finding help (Attachment 1).
| Dimension | Analyze content | Opportunities and challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Political | Policy support: China's "14th Five-Year Plan" focuses on supporting biomedical innovation. Hangzhou's "Eagle Plan" may provide entrepreneurial funding. Regulatory barriers: the approval cycle of the third category of medical apparatus is long (3-5 years), and it needs to be strictly reviewed by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). |
Opportunity: Accelerate approval through green channel. Challenge: High compliance costs. |
| Economic | Market size: The global ophthalmic drug market is expected to reach 46 billion dollars by 2025, and China's annual growth rate will exceed 15%[8] [9]. Cost pressure: Patients in developing countries have limited payment ability and need to reduce costs through large-scale production. |
Opportunity: Potential for medical insurance coverage. Challenge: High price sensitivity. |
| Social | Aging trend: The proportion of the population over 60 years old in China has reached 20%, and the incidence of cataracts increases significantly with age. Increased health awareness: Consumers' preference for non-invasive treatments has increased. |
Opportunity: Precise positioning of the elderly market. Challenge: Insufficient primary medical education. |
| Technological | Breakthrough in synthetic biology: CRISPR engineering bacteria, targeted delivery technology, and other synthetic biology methods have matured. Competing product threat: Novartis, Alcon and other pharmaceutical companies layout nano eye drops, but lack of long-term sustained-release solutions. |
Opportunity: Technological differentiation. Challenge: Patent barriers need to be broken through. |
| Environmental | Sustainable production: Hydrogel materials must meet biodegradable standards to avoid microplastic pollution. Carbon footprint management: Hangzhou Pharmaceutical Port Town requires companies to pass green factory certification. |
Opportunity: Environmental protection brand premium. Challenge: High cost of degradable materials. |
| Legal | Biosafety Law: Engineering bacteria must meet the dual physical packaging requirements of the Biosafety Law. Intellectual property rights: Need to lay out core patents (such as RNF114 targeted modification technology). |
Opportunity: Policy compliance enhances trust; Challenge: Complex international patent layout. |
Competitive Analysis Based on Porter's Five Forces Model
Model
New
Entrants
Substitutes
Power of
Buyers
Power of
Suppliers
Among
Existing
Competitors
| Five forces dimension | Analyze content | Threat level to the project | Response strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rivalry among existing competitors |
Main competitors: traditional cataract surgery (Aier Eye Hospital, Novartis), nano eye drops (such as Novartis' Xiidra). Competition focus: treatment cost, convenience, safety. Status: Surgery is the gold standard, but the quota is uneven; the effect of eye drops is limited. |
Medium to high | Differentiated competition: Focus on "non-surgical + long-acting sustained-release", avoid direct competition with the surgical market, and focus on developing countries and contact lens users. |
| Bargaining power of suppliers |
Key suppliers: bio-hydrogel materials (PVA/hyaluronic acid), engineered bacterial chassis (Shuffle Escherichia coli), fluorescent protein (Crimson). Supplier concentration: Material suppliers are scattered, and engineering technology relies on cooperation with universities. |
Low | Vertical integration: Collaborate with the School of Materials Science and Technology at Zhejiang University to develop self-developed hydrogels and reduce external dependence. |
| Bargaining power of buyers |
Hospitals/clinics: price-sensitive to innovative medical apparatus, but demand is rigid (developing countries urgently need alternatives). Consumers: Individual users are price-sensitive, but can be bound to medical insurance or public welfare subsidies. |
Medium | Tiered pricing: Hospitals purchase at high prices (covering R & D costs), while developing countries provide a public welfare version (simplifying functions). |
| Threat of substitutes |
Direct substitution: gene therapy (such as CRISPR editing of lens cells), stem cell regeneration technology (still in the laboratory stage). Indirect substitution: upgraded version of traditional eye drops (such as nanoliposome delivery). |
Low to medium | Technical Competitive Edge: Accelerate patent layout (6 core patents have been planned), establish a dual barrier of "slow-release technology + engineering bacteria". |
| Threat of new entrants |
Entry barriers: three types of medical apparatus approval (3-5 years), synthetic biology technology threshold, large-scale production costs. Potential entrants: Multinational pharmaceutical companies (such as Johnson & Johnson and Bausch & Lomb) may enter through acquisitions or generics. |
Medium | First-mover advantage: Seize the market through rapid clinical trials (in conjunction with Hangzhou Food and Drug Administration's green channel) and bind research and development resources from universities. |
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- World's first "engineered bacteria + contact lenses" treatment platform
- Multiple indications for expansion (dry eye, glaucoma)
- Strong support from Zhejiang University's industry-university-research resources
Weaknesses
- Engineering bacteria stability needs optimization for single pair usage duration
- Treatment effectiveness requires further experimental verification
- Complex mass production process
- Insufficient international patent layout
Opportunities
- Intensifying aging population and increasing patient numbers
- Urgent non-surgical needs in developing countries
- SDGs driving inclusive healthcare investment
Threats
- Industry giants' monopoly on eye drops market
- High European Union compliance costs
- Patient skepticism about live engineering bacteria
Potential partners
planning to cooperate deeply with a certain enterprise, below are the enterprises that we might look into:
| Type | Company/Organization | Cooperation Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Companies | Huadong Medicine (Hangzhou) | Jointly develop ophthalmic drug delivery systems and share clinical trial resources. |
| Qiming Medical (Hangzhou Medical Port) | With the help of its medical apparatus industrialization experience, accelerate product landing. | |
| Contact Lens Manufacturers | Johnson & Johnson | Technology licensing cooperation, integrating its global distribution network. |
| Bausch & Lomb | Jointly launched the "therapeutic contact lens" brand to seize the high-end market. | |
| Research Institutions | Zhejiang University School of Medicine and The Second Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University (which is the most prominent among all affiliated hospitals in ophthalmology) | Obtain clinical data, understand the market, and conduct preclinical research. |
| Investment Institutions | Hillhouse Capital | Focusing on early-stage investment in medical technology, potential A-round lead investor. |
| ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center | Provide funds in the early stages of our project. |
Source of Investment
To ensure that the funding needs of the project are met at different stages of development, we have designed diversified financing paths. In the early stage (seed round), we will seek funding from Zhejiang University Alumni Fund (such as Zhejiang University Network New Venture Capital), ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center, and Hangzhou's "Young Eagle Plan", mainly for prototype development and preliminary experiments. In the mid-term stage (Series A), we will seek support from venture capital institutions such as Hillhouse Capital and Sequoia China, as well as strategic investments from pharmaceutical companies such as Huadong Medicine. The funds will be used for clinical trials and production line construction. In the later stage (Series B and IPO), we plan to attract international capital (such as Temasek Holdings) and promote listing on the Science and Technology Innovation Board to support global market expansion and brand internationalization.
Marketing & implementation
Analysis of user requests
Core target group - cataract patients
1. Number of cataract patients
In China, the incidence of cataracts increases significantly with age. According to a study conducted in the suburbs of Shanghai, the incidence of cataracts in the population aged 65 and above was 57.0%. Another study showed that the incidence of cataracts in the population aged 45 and above in rural western China was 45.15%[1]-[2].
2. Surgical coverage
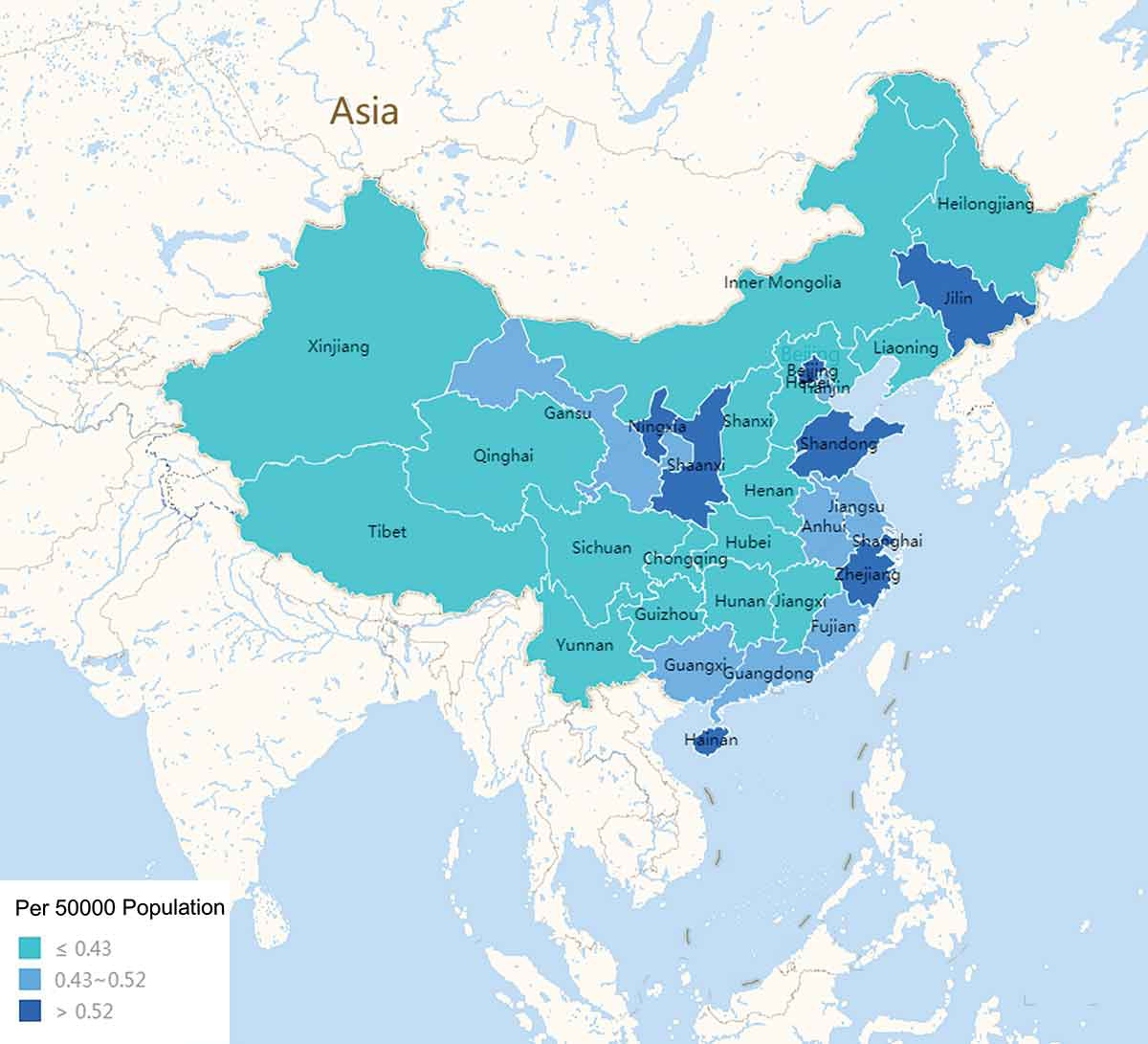
In China, the coverage rate of cataract surgery is still low. According to a national study, the proportion of cataract surgery between 2011 and 2015 was only 1.22%. In the suburbs of Shanghai, the coverage rate of cataract surgery among people aged 65 and above is 10.9%. In rural areas of the southwest, the cataract surgery coverage rate (CSC) is 53.3%, but there are still a large number of patients who have not undergone surgery[3] [4]. What's more, there exists an apparent inequality in access, below is the figure that shows the distribution of cataract surgeons per 50,000 population in China in 2014.[10]
3. Prevalence of dry eye syndrome among contact lens users
Dry eye syndrome has a high incidence in China. According to a multicenter cross-sectional study, the incidence of dry eye syndrome has significantly increased among contact lens wearers. The study showed that the incidence of dry eye syndrome increased significantly among users who wore contact lenses for more than 3 years[5].
Urgent needs and existing pain points:
The high cost of cataract surgery and the uneven distribution of medical resources are indeed major issues. The low absorption rate of traditional eye drops (< 5%) and the need for frequent use (6-8 times a day) are also significant pain points.
Marketing strategy
Target market segmentation: We divide the market into core and secondary groups. The core group includes cataract patients, with a special focus on developing countries (such as India and Africa) and countries with severe aging (such as China and Japan). Among them, we will use China as the starting point of our project's market. In addition, the high-risk group of dry eye syndrome, such as young white-collar workers and contact lens wearers who use electronic devices for a long time, is also our focus. The secondary group covers medical institutions (such as hospitals and clinics) and public welfare organizations (such as the International Association for the Prevention of Blindness) to expand the social impact of the product.
Value proposition: Our core message focuses on three major highlights: firstly, "non-surgical treatment", with the slogan "Say goodbye to surgical knives, weekly disposable lenses reverse cataracts", emphasizing the innovation of the product; secondly, "long-lasting convenience", conveying the convenience of product use through "one-time wear, continuous treatment"; finally, "combination therapy", highlighting the multiple effects of "one lens, simultaneously solving cataracts and dry eye syndrome", meeting the comprehensive needs of different patients.
Channel strategy: In the B2B field, we will cooperate with top Hospitals to strive to include our products in the medical insurance catalog and quickly enter the medical market through existing channels of partners such as Huadong Medicine and Qiming Medical. In the B2C field, we plan to open flagship stores on e-commerce platforms such as Tmall and JD.com Health, providing subscription services for monthly delivery. At the same time, we will set up product experience counters in offline chain pharmacies to enhance consumers' experience.
Promotion strategy: In terms of promotion, we will combine three strategies: authoritative endorsement, digital marketing, and public welfare linkage. Firstly, we plan to invite Professor Yao Ke from the School of Medicine of Zhejiang University to release clinical trial data, enhance the credibility of the technology, and jointly release the "White Paper on Non-Surgical Treatment of Cataracts" with the medical department of Zhejiang University to enhance international influence. Secondly, we will carry out digital marketing, launch a popular science short video "3 Minutes to Understand Your Eyes" through digital platforms like Douyin, strive to break through 100,000 + views and share real wearing experiences with KOL on REDNOTES to create hot topics such as #Contact Lenses for Cataract #. Finally, we will implement the "Buy One Donate One" public welfare plan, donating a public welfare version of the product to patients in Africa or remote rural areas in China for every lens sold, balancing commercial value and social responsibility.
Pricing strategy: In terms of pricing, we will adopt a differentiated strategy. For the high-end market, weekly disposable lenses are priced at 300 or more yuan per lens, referring to Johnson & Johnson's pricing system (attachment 1), while considering the therapeutic value and production cost of the product.
In developing countries, we will provide public welfare products that are sold at cost or partially covered by government subsidies and donations to reduce the burden on patients. In addition, we will launch a subscription discount policy, where customers can enjoy a 10% discount for 6 consecutive months, thus binding long-term users.
Implementation strategy
1. Phased Implementation
Pilot Phase
- Conduct clinical trials in 3 tier-1 hospitals in Hangzhou
- Cover 500 patients and accumulate initial data
- Open online pre-sale channel with Ali Health
- Collect first batch of user feedback
Expansion Phase
- Establish GMP factory in Hangzhou Pharmaceutical Port
- Achieve annual production capacity of 10 million units
- Expand to markets like India and Kenya
- Collaborate with local medical institutions
Globalization Stage
- Complete FDA and CE certification
- Enter European and American markets
- Develop extended product lines (glaucoma, retinopathy)
- Expand business territory globally
2. Partner Ecosystem
Research & Development
Establish "Ophthalmic Slow-Release Technology Joint Laboratory" with Zhejiang University School of Medicine to promote technological innovation and collaborate with existing labs specializing in hydrogels and cataracts.
Production
Leverage Hangzhou Medical Port Town's resources to create a green production system and optimize supply chain management.
Public Welfare
Partner with International Association for the Prevention of Blindness (IAPB), participate in global anti-blindness programs, and expand brand social influence.
3. User Support System
Digital Support
- "ClearLens Assistant" Mini Program with video tutorials
- Online consultation service
- 24/7 customer service hotline (400)
After-sales Service
- Follow-up questionnaires (Day 7 & 30)
- Continuous product optimization
- "Worry-free return and exchange" policy with 30-day refund protection
4. Innovative Thinking
Considering the long and complex approval cycle of medical apparatus, we realize that clinical application still needs time. Therefore, we have decided to shift part of our focus to the potential of scientific research and explore the promotion value of non-clinical products.
Microengineered Biomimetic Ocular Models is the first of its kind, as we did not find any other in vitro devices for anterior whole-layer simulation of the lens.
What's more, we have also designed and constructed a device that integrates fluorescence signal detection technology with a black contact lens container. By pressing a button, the light source will stimulate the fluorescent protein Crimson, and the fluorescence intensity will be monitored by the BH1750 sensor.
It not only has innovative technical characteristics, but also can provide support for future medical development as a scientific research tool.
Our project has demonstrated its huge potential in technological innovation and scientific research. We believe that over time, these innovations will gradually be integrated into practical applications and bring positive social impacts. In this way, we not only contribute technically, but also take firm steps in promoting sustainable development in the medical field.
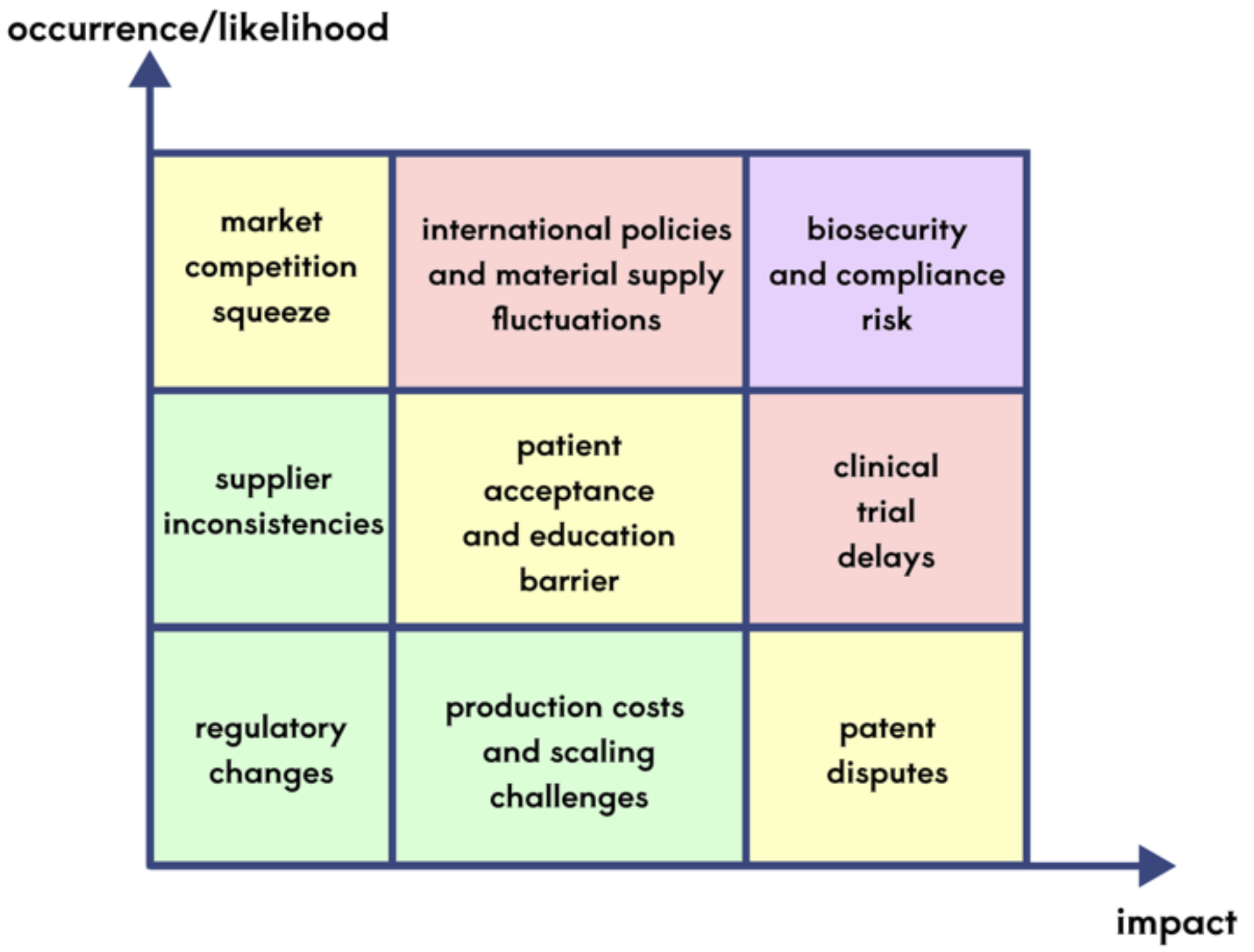
Risk Analysis
Deterministic Analysis
Deterministic risk refers to risks that are clearly present and can be partially or fully controlled by existing strategies.
Biosecurity and compliance risks: Engineering bacteria leakage may cause ecological or health problems. Although the risk has been greatly reduced through hydrogel packaging and biosafety reporting to the pathway design, strict monitoring of the production environment is still required during the mass production stage. In addition, the approval cycle for the third type of medical apparatus is long (3-5 years), and it needs to rely on the "green channel" policy of the Hangzhou Medical Products Administration to accelerate the process. If the policy support is insufficient or the regulations change, the product may be delayed.
Production costs and scaling challenges: The production cost of bio-hydrogels and engineering bacteria is relatively high, especially in the initial stage of scale. For example, non-petroleum-based alternative materials for polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) are not yet fully mature, and dependence on imports may lead to supply chain fluctuations. By cooperating with Huadong Medicine to optimize the production process and taking advantage of tax incentives at Hangzhou Medical Port, some cost pressures can be hedged, but the profit margin may still be lower than expected in the short term.
Market competition squeeze: Traditional surgery and nano eye drops are still the mainstream solutions. If giants like Novartis launch similar sustained-release technology products in advance, it may dilute the market uniqueness of ClearLens ®. By rapidly advancing patent layouts (such as RNF114 targeted modification technology) and binding hospital channels, a first-mover advantage can be built, but continuous investment in research and development is still needed to maintain technological leadership.
Uncertainty risk
Uncertainty risk refers to external factors that are difficult to quantify or predict and require dynamic adjustment.
Patient Acceptance and Educational Barriers: Although the project conducts market education through public welfare screening and endorsement by KOL doctors, some patients still have doubts about "live engineering bacteria", especially in areas with low cultural levels or conservatism. If the initial clinical trial data (such as 5% stimulating feedback) is amplified and disseminated, it may affect brand trust. A real-time Public Opinion Monitoring system needs to be established, and concerns should be alleviated through transparent disclosure of safety data (such as third-party biosafety reports).
Technology substitution and disruptive innovation: Gene therapy or stem cell regeneration technology may directly overturn existing treatment plans if breakthroughs are made in the next 5 years. Projects need to maintain technological scalability, such as reserving interfaces to support future integration of gene therapy modules or supplementing technical gaps through mergers and acquisitions of start-ups.
International policies and supply chain fluctuations: The certification requirements for degradable materials under the European Union REACH regulation may be upgraded, leading to increased export costs. Geopolitical conflicts may also affect the global supply chain of SHuffle's engineering bacteria chassis. Therefore, it is necessary to establish redundant production lines at Hangzhou Medical Port and reserve key raw materials for 3-6 months in advance.