We used the pET-32a(+) plasmid to construct HA protein and RNF114 protein separately. The specific construction process is as follows:
-
Construction of RNF114 protein: To express the RNF114 protein, we constructed the following multi-promoter gene expression system:
pelB - GS-linker*1 - TAT - GS-linker*1 - Target Peptide - GS-linker*5 - GALA3 - Rigid linker(EAAAK)*3 - GS-linker*2 - GFP - BBa_J61107 (RBS2) - Crimson - T7 terminator.
- Among them, the pelB sequence is mainly used for the secretion of the RNF114 protein, the TAT sequence is used to enhance the protein's transmembrane (corneal) capability, and GALA helps to enhance its stability within the cells. Crimson, as a marker gene, is used to track the expression of the protein in experiments.
-
Construction of HA: In order to express HA, we constructed the following gene expression system:
T7 promoter - lac operator - Shine-Dalgarno (RBS1) - hasA - BBa_J61107 (RBS2) - hasB - T7 terminator。
- 4. This construct utilizes the strong T7 promoter to ensure efficient expression of the protein in Escherichia coli.
We used the pET-32a(+) plasmid to construct HA protein and RNF114 protein separately. This system employs the T7 promoter for strong promoter-driven expression. Shine-Dalgarno (RBS1) and BBa_J61107 (RBS2) serve as ribosome binding sites to assist RNA polymerase in recognizing and efficiently initiating transcription.
RF114
-
Construction of RNF114 protein: In order to express RNF114 protein, we constructed the following gene expression system:
Gene expression system during production:T7 promoter - lac operator - Shine-Dalgarno (RBS1) - pelB - GS-linker*1 - TAT - GS-linker*1 - Target Peptide - GS-linker*5 - GALA3 - rigid linker(EAAAK)*3 - RNF114 - BBa_J61107 (RBS2) - Crimson - T7 terminator。
.png)
Gene expression system for validation and testing experiments:T7 promoter - lac operator - Shine-Dalgarno (RBS1) - pelB - GS-linker*1 - TAT - GS-linker*1 - Target Peptide - GS-linker*5 - GALA3 - rigid linker(EAAAK)*3 - RNF114 - rigid linker(EAAAK)*3 - GS-linker*2 - GFP -BBa_J61107 (RBS2) - Crimson - T7 terminator.
.png)
-
The connection between pelB, TAT and target peptide
We first analyzed the structure of the RNF114 protein.
N-terminus: There is a relatively conserved amino acid sequence in the N-terminal region, and its function may involve protein stability, subcellular localization, or interaction with other proteins.
C-terminus: The C-terminus of RNF114 contains a RING finger domain, which is directly involved in its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. The C-terminal RING structure is the key region for binding to the E2 ubiquitin enzyme. Through this domain, RNF114 can transfer ubiquitin molecules from the E2 ubiquitin enzyme to the target protein, thereby achieving ubiquitination tagging and regulating the degradation or functional regulation of the substrate.
N-terminal structure: In short, the N-terminal principle is the RING finger domain. Connecting short peptides to the N-terminal can avoid affecting the spatial structure of the RING finger domain, which is the active region of RNF114. Therefore, we choose to connect as many short peptides as possible to the N-terminal. Between the short peptides (TAT, pelB, GALA), we use flexible linkers (GGGGS) with different copy numbers to connect. The specific structure is:pelB - GS-linker*1 - TAT - GS-linker*1 - dock - GS-linker*5 - GALA。Between GALA and RNF114, we use a three-segment rigid linker (EAAAK) to connect them. The structure is as follows::GALA - rigid linker(EAAAK)3 - RNF114。In summary, the structure of the N-terminus is as follows:pelB - GS-linker*1 - TAT - GS-linker*1 - dock - GS-linker*5 - GALA - rigid linker(EAAAK)*3 - RNF114.
C-terminal structure: In order to quickly monitor the expression of RNF114 during the experimental stage, we connected GFP (green fluorescent protein) to the C-terminus of RNF114 protein through multiple copies of rigid linker + flexible linker. The structure is as follows: RNF114 - rigid linker(EAAAK)*3 - GS-linker*2 - GFP.
Verification of RNF114 protein structure:
In order to verify the structure of the recombinant RNF114 protein, I used AlphaFold3 to predict the three-dimensional structure of the recombinant protein. Then, I used the align function in PyMOL to compare the structures of the original RNF114 protein and the recombinant RNF114 protein. The comparison results are as follows:
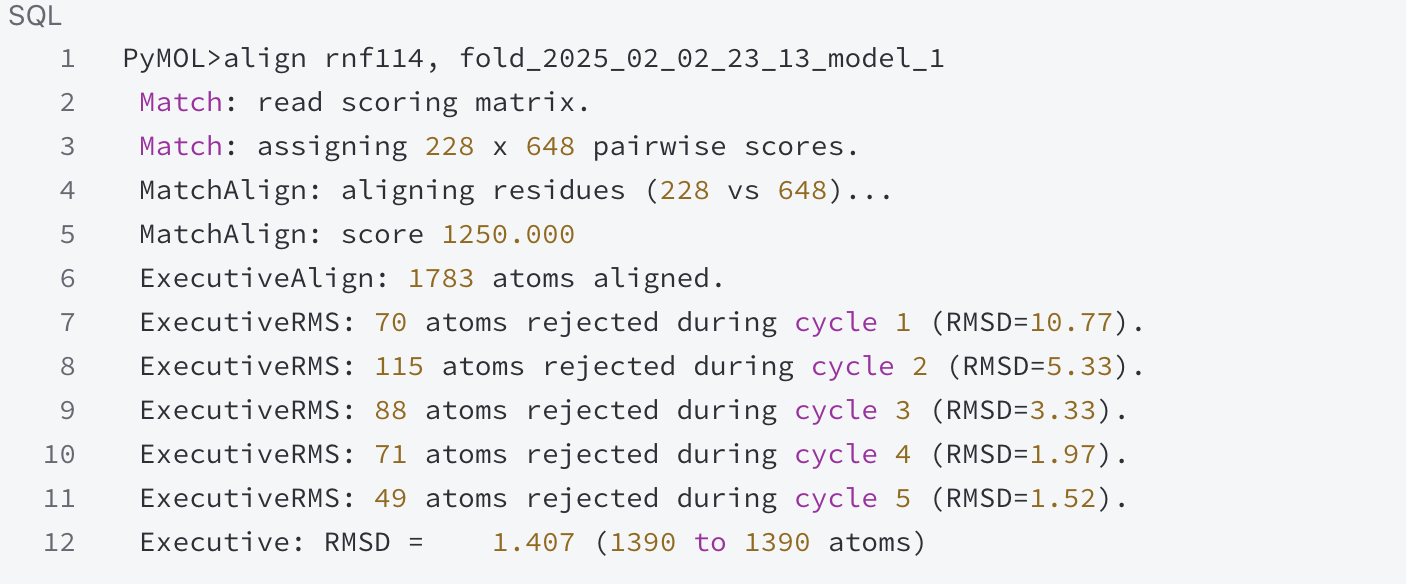
During the comparison process, the scoring matrix was used to score the pairing of 228 residues with 648 residues, and the alignment score was calculated to be 1250.000. After comparison, 1783 atoms were successfully aligned. Through multiple alignment cycles, the RMSD values of each round were calculated step by step. In the first cycle, 70 atoms were not aligned, and the RMSD value was 10.77; 115 atoms were rejected in the second round, and the RMSD value dropped to 5.33; 88 atoms were not aligned in the third round, and the RMSD was 3.33; 71 atoms were rejected in the fourth round, and the RMSD was 1.97; in the fifth round, 49 atoms were excluded, and the RMSD was 1.52. The final RMSD value was 1.407, indicating that the structure of the recombinant RNF114 is very similar to that of the original RNF114.
This analysis shows that the recombinant protein and the original RNF114 protein have a high degree of similarity in three-dimensional structure, and the differences are mainly concentrated in some local connections between functional short peptides (TAT, pelB, GALA) and GFP, and these differences will not significantly affect the folding of the overall structure of RNF114.
The following picture shows the structure of the original RNF114 and the recombinant RNF114:
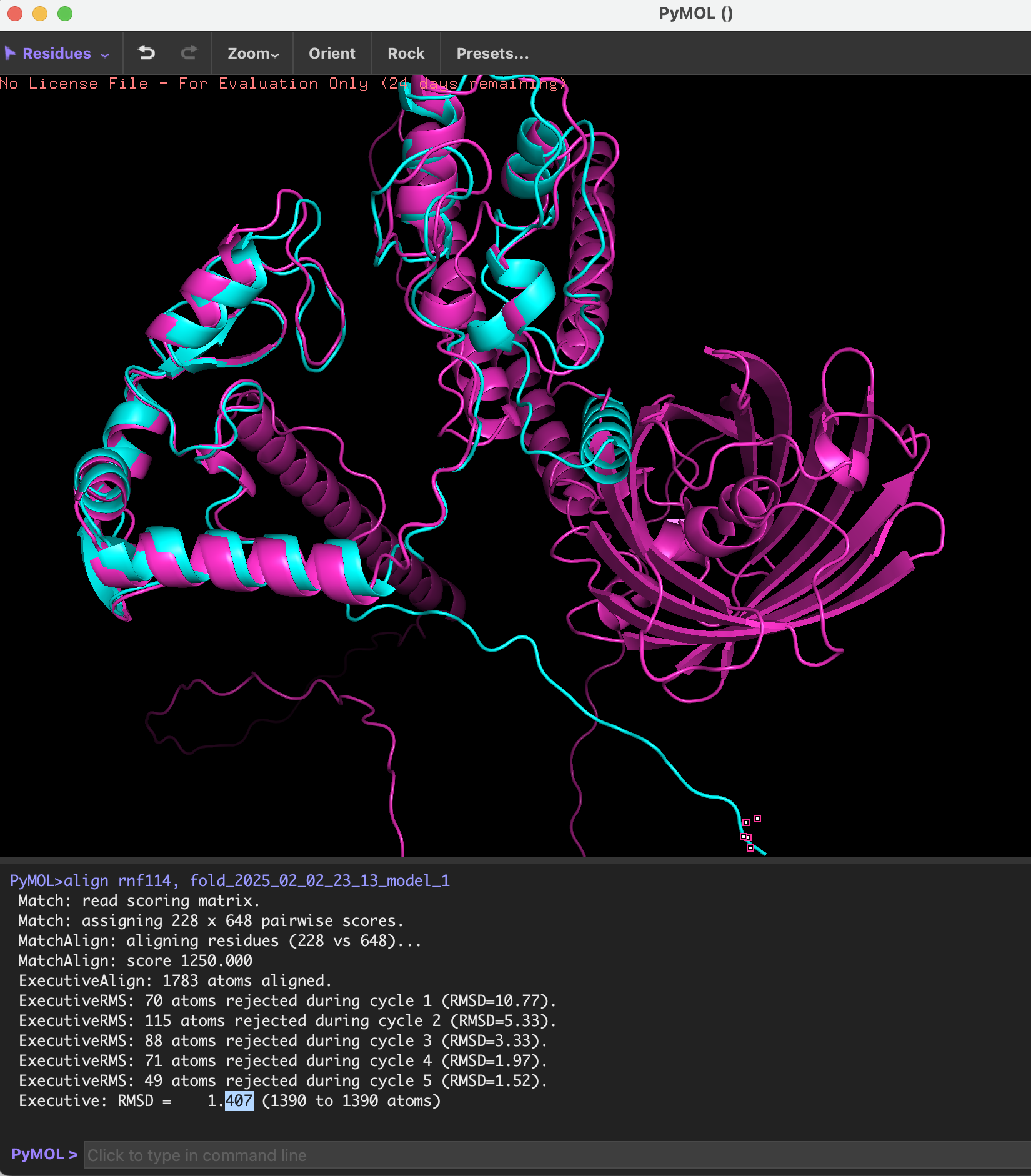
-
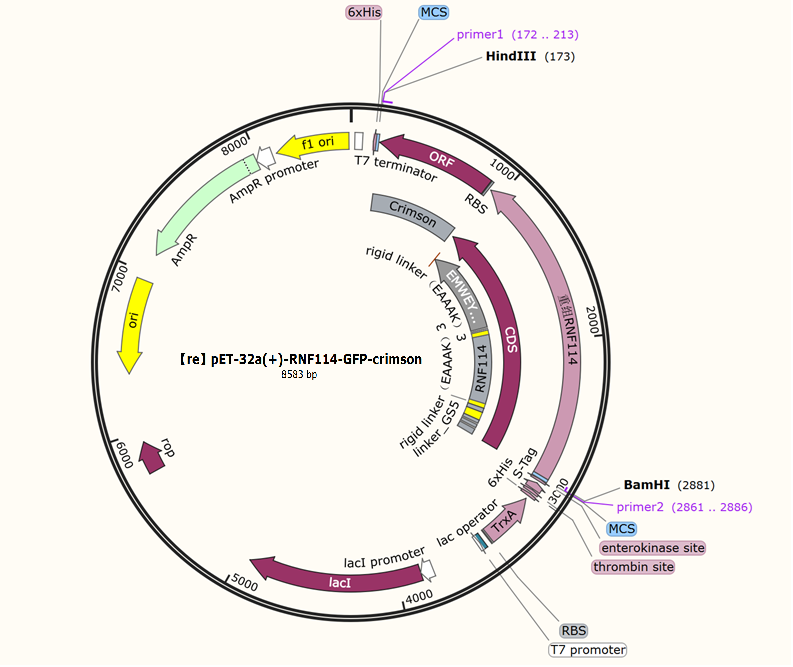
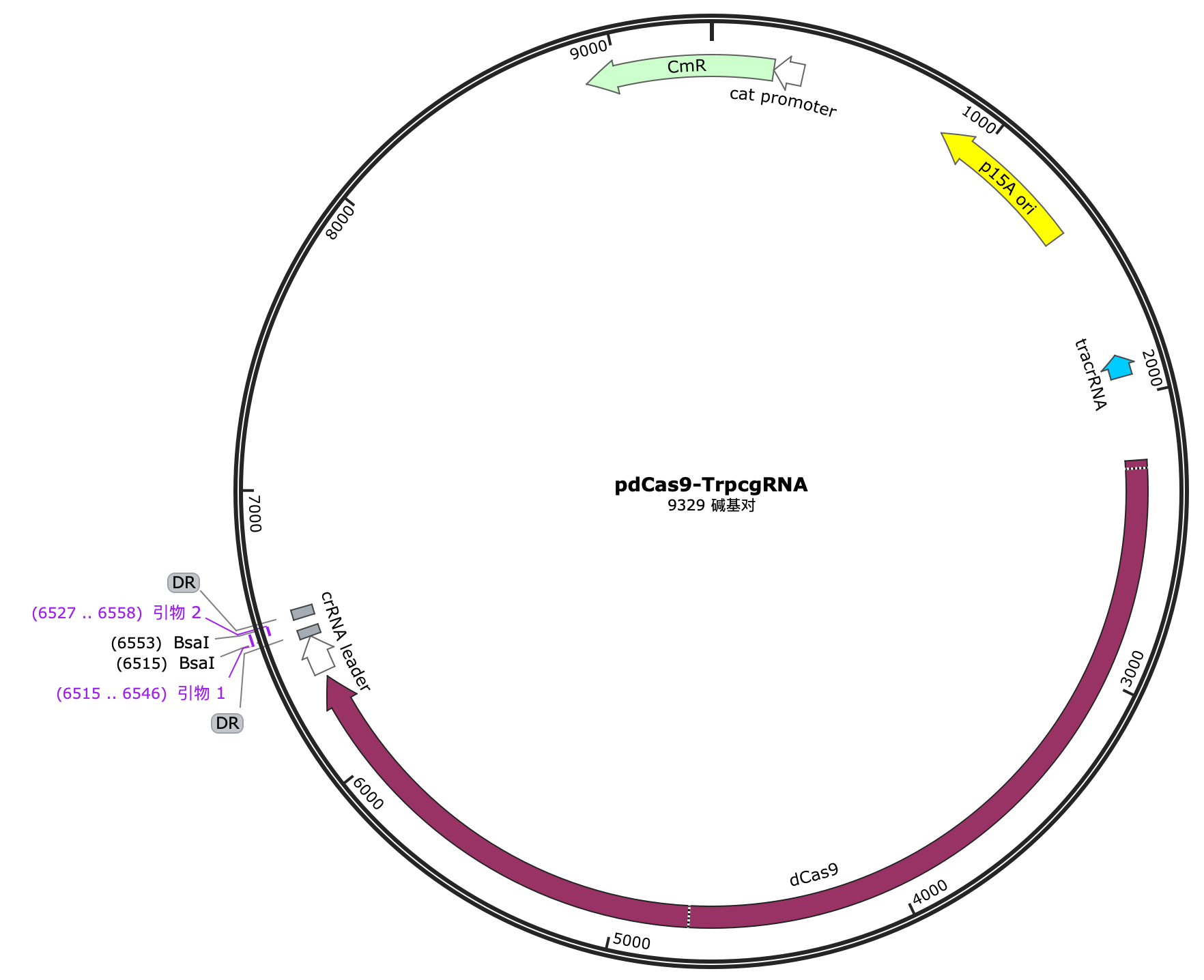
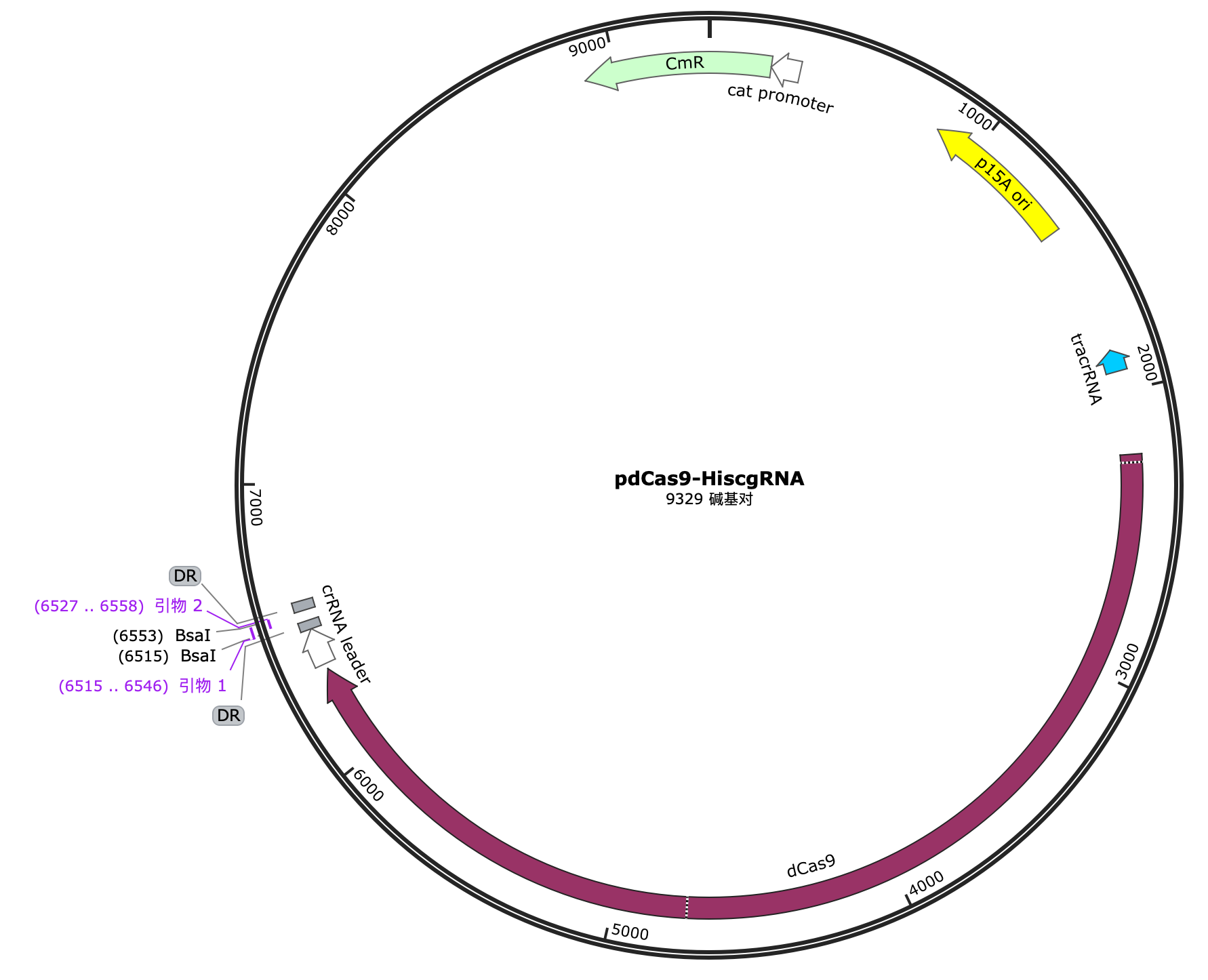
Selection and construction of recombinant plasmid
We selected the pET-32a(+) plasmid, connected the recognition sequences of BamHI and HindIII restriction endonucleases at both ends of the recombinant RNF114 by PCR, and introduced them into the MCS region of pET-32a(+) by double enzyme digestion to construct the pЕТ-32a(+)-RNF114-GFP-crimson recombinant plasmid.
.png)
HA
-
Construction of HA: In order to express HA, we constructed the following gene expression system
T7 promoter - lac operator - Shine-Dalgarno (RBS1) - hasA - BBa_J61107 (RBS2) - hasB - T7 terminator
.png)
hasA and hasB are two enzymes encoded by Streptococcus equisimilis, namely UDP-glucose dehydrogenase and hyaluronan synthase, which work together to synthesize hyaluronic acid (HA).
hasA: Encodes UDP-glucose dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the conversion of UDP-glucose into UDP-gluconic acid, providing a precursor molecule for the synthesis of HA.
hasB: Hyaluronan synthase is responsible for catalyzing the polymerization of UDP-glucose to form hyaluronan.
In this study, these two genes were co-expressed to continuously produce HA, achieving efficient production and long-term release of HA, thereby providing a long-lasting lubricating effect.
-
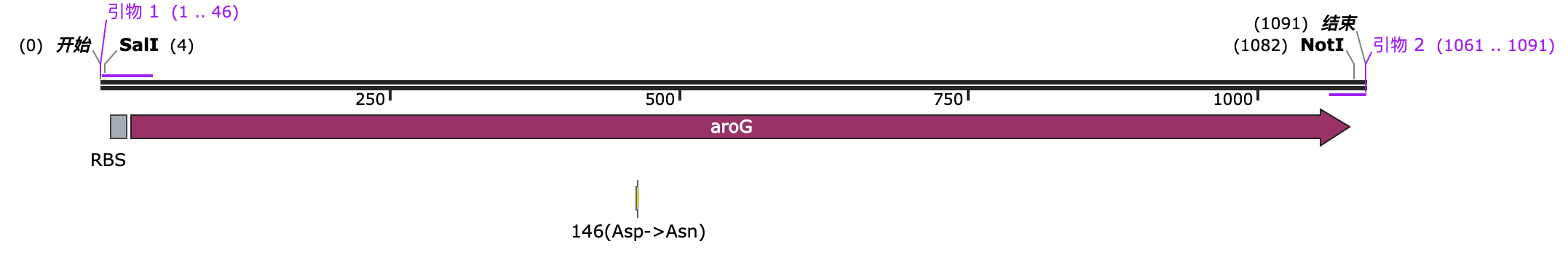
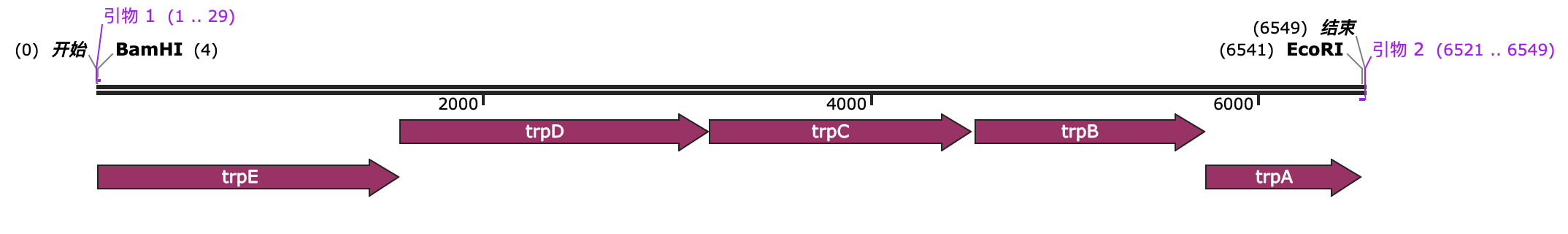
Construction of expression vector for HA expression
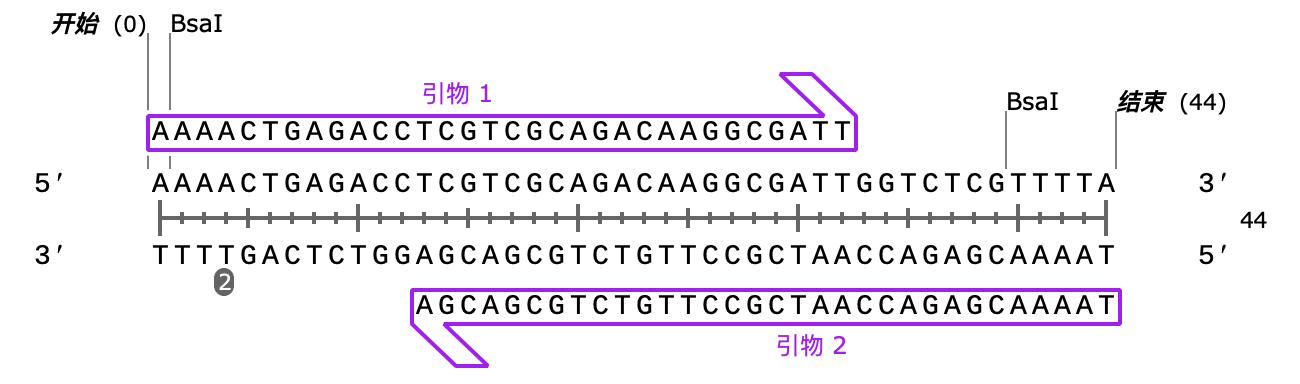
We selected the pET-32a(+) plasmid, connected the recognition sequences of EcoRI and BamHI restriction endonucleases at both ends of the HA protein through PCR, and introduced them into the MCS region of pET-32a(+) through double enzyme digestion to construct the pET-32a(+)-hasAB recombinant plasmid.
.png)


.png)
.png)
.png)